Sex education in schools sparks much debate. What should be taught?
Sex education is a crucial part of a child's learning journey. It shapes their understanding of relationships, consent, and personal health. But what topics are appropriate for the classroom? Parents, educators, and policymakers often clash over this. Some argue for a comprehensive curriculum that covers everything from anatomy to emotional aspects.
Others prefer a more limited approach. Ethical considerations further complicate the issue. Religious beliefs, cultural values, and societal norms all play a role. The goal is to provide students with the knowledge they need while respecting diverse perspectives. This blog will explore the ethical dilemmas and suggest what should be included in school sex education programs. Stay tuned for an insightful discussion.
Credit: www.the74million.org
Importance Of Sex Education
Sex education in schools is a sensitive yet vital topic. The question often arises: What should be taught? Understanding the importance of sex education is crucial for several reasons. It helps students make informed decisions, promotes healthy relationships, and addresses misconceptions. Proper sex education can lead to a well-rounded understanding of human sexuality and its implications.
Benefits For Students
Sex education offers numerous benefits for students. It equips them with the knowledge to make safe choices, understand their bodies, and respect others. Here are some key benefits:
- Informed Decision-Making: Students learn about contraception, consent, and safe sex practices. This knowledge helps them avoid unwanted pregnancies and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Healthy Relationships: Lessons on communication, respect, and boundaries help students build positive relationships. They learn to identify unhealthy behaviors and seek help if needed.
- Self-Awareness: Students become aware of their own bodies and feelings. This understanding fosters self-respect and confidence.
- Mental Health: Discussing topics like puberty and emotions can reduce anxiety and promote mental well-being.
Consider the following table that highlights the benefits of sex education:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Informed Decision-Making | Understanding contraception and safe sex practices |
| Healthy Relationships | Building respectful and positive relationships |
| Self-Awareness | Gaining knowledge about one's body and feelings |
| Mental Health | Reducing anxiety and promoting well-being |
Impact On Public Health
Sex education does not only benefit individual students. It also has a significant impact on public health. Comprehensive sex education can lead to healthier communities. Here are some key points:
- Reduction in STIs: Educated individuals are more likely to use protection, reducing the spread of STIs.
- Lower Teen Pregnancy Rates: Access to accurate information and contraceptive methods leads to fewer teen pregnancies.
- Better Health Outcomes: Informed individuals are more likely to seek medical help when needed, leading to early detection and treatment of health issues.
- Economic Benefits: Lower rates of STIs and teen pregnancies reduce healthcare costs, benefiting the economy.
The following table illustrates the impact of sex education on public health:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduction in STIs | Increased use of protection and safer sex practices |
| Lower Teen Pregnancy Rates | Access to contraceptives and accurate information |
| Better Health Outcomes | Early detection and treatment of health issues |
| Economic Benefits | Reduced healthcare costs and economic burden |
Credit: www.the74million.org
Curriculum Approaches
Sex education in schools is a topic that sparks much debate. What should be taught? The curriculum approaches vary widely. Some advocate for abstinence-only programs, while others support comprehensive sex education. Understanding these approaches helps in discussing the ethics involved.
Abstinence-only Programs
Abstinence-only programs focus on teaching students to refrain from sexual activity until marriage. These programs emphasize the moral, health, and social benefits of abstinence.
Key points of abstinence-only education include:
- Promoting abstinence as the only sure way to avoid pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Teaching that abstinence is the expected standard for all school-age children.
- Highlighting the potential psychological and physical harms of premarital sexual activity.
Some argue that abstinence-only programs can be effective. They believe these programs encourage students to make responsible choices. However, critics say that these programs often leave out important information.
For example, these programs may not teach about contraception methods. This lack of information can lead to higher rates of unintended pregnancies and STIs. The debate continues on whether abstinence-only education is the best approach.
Comprehensive Sex Education
Comprehensive sex education covers a broader range of topics. These programs include information on abstinence as well as contraception, consent, and healthy relationships.
Components of comprehensive sex education include:
- Discussing various methods of contraception and their effectiveness.
- Providing information on how to prevent STIs and unintended pregnancies.
- Teaching students about consent and respectful relationships.
- Including discussions on sexual orientation and gender identity.
Proponents of comprehensive sex education argue that it prepares students better for real-life situations. Students learn to make informed decisions about their bodies and relationships. They get a well-rounded understanding of sexual health.
Some evidence suggests that comprehensive programs can lead to lower rates of teen pregnancies and STIs. Critics worry that discussing contraception and sexual orientation might encourage sexual activity among teens. The effectiveness and appropriateness of comprehensive sex education remain key points in the ongoing debate.
Cultural Sensitivity
Sex education in schools is a topic that often sparks debate. One key aspect of this debate is cultural sensitivity. It's important to consider the diverse backgrounds and beliefs of students. This ensures that the curriculum is respectful and inclusive. Below, we explore two important areas related to cultural sensitivity in sex education: diverse backgrounds and religious considerations.
Diverse Backgrounds
Students come from a variety of cultural backgrounds. Each culture has its own beliefs and practices related to sex and sexuality. Educators need to be aware of these differences to create an inclusive environment.
Here are some ways to address diverse backgrounds in sex education:
- Inclusive Language: Use language that respects all cultures. Avoid stereotypes and generalizations.
- Multicultural Resources: Provide materials that reflect various cultural perspectives. This can include books, videos, and guest speakers.
- Community Involvement: Engage with parents and community leaders. Their input can help shape a curriculum that respects cultural values.
Consider the following table for a quick overview of how to address diverse backgrounds:
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Inclusive Language | Using respectful and non-stereotypical language |
| Multicultural Resources | Providing diverse and culturally relevant materials |
| Community Involvement | Engaging with parents and leaders for insights |
Religious Considerations
Religion plays a significant role in many students' lives. Different religions have distinct views on sex and sexuality. Respecting these views is crucial in sex education.
Here are some ways to address religious considerations:
- Respect for Beliefs: Acknowledge and respect different religious beliefs. Avoid content that might be offensive.
- Optional Participation: Allow students to opt-out of certain lessons. This respects their religious beliefs and values.
- Interfaith Dialogue: Encourage open discussions about various religious perspectives. This promotes understanding and respect among students.
Consider the following table for a quick overview of how to address religious considerations:
| Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Respect for Beliefs | Acknowledging and respecting different religious views |
| Optional Participation | Allowing students to opt-out of certain lessons |
| Interfaith Dialogue | Encouraging open discussions about religious perspectives |
Parental Involvement
Sex education in schools is a crucial topic, sparking many debates about what should be taught. Parental involvement is one of the most discussed aspects. Parents often have strong opinions about the content of sex education. They play a vital role in shaping their children's understanding and values around this sensitive subject. It's important to find a balance that respects diverse views while ensuring that students receive accurate and comprehensive information.
Communication Strategies
Effective communication between schools and parents is key. Schools should create clear channels for dialogue, ensuring parents are well-informed about the sex education curriculum. This can be achieved through various methods:
- Parent-Teacher Meetings: Regular meetings provide a platform for discussing the curriculum and addressing concerns.
- Newsletters: Monthly or quarterly newsletters can keep parents updated on what is being taught.
- Workshops: Hosting workshops for parents can help them understand the curriculum and how to discuss these topics with their children.
- Surveys: Anonymous surveys can gauge parental opinions and feedback on the sex education program.
Additionally, schools can use digital tools to enhance communication. For instance:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Emails | Send detailed information and updates |
| School Website | Provide resources and curriculum details |
| Social Media | Share quick updates and engage with parents |
These strategies ensure that parents are not left in the dark and can actively participate in their children's education.
Balancing Perspectives
Balancing different perspectives is crucial in sex education. Parents come from various cultural, religious, and personal backgrounds, which influence their views on what should be taught. Schools need to navigate these differences carefully to create an inclusive environment.
One way to achieve this balance is through inclusive curriculum design. This involves:
- Consulting a diverse group of parents and stakeholders during curriculum development.
- Including different viewpoints and cultural perspectives in the curriculum.
- Ensuring that the curriculum covers a broad range of topics like consent, healthy relationships, and safe practices.
Another approach is through flexible policies. Schools can offer opt-out options for parents who do not want their children to participate in certain lessons. This respects parental authority while still providing comprehensive education for those who choose to participate.
Additionally, schools can create supportive environments by training teachers to handle sensitive topics with empathy and respect. Teachers should be prepared to address questions and concerns from both students and parents.
By considering these strategies, schools can ensure a balanced approach that respects diverse perspectives while providing essential education.
Teacher Training
Effective sex education in schools depends heavily on the training and preparedness of teachers. Teacher training is a cornerstone for delivering accurate, respectful, and comprehensive sex education. Educators must be well-equipped to handle sensitive topics and diverse student needs. The right training ensures that they can create a safe and inclusive learning environment.
Qualifications Needed
The qualifications needed for sex education teachers are crucial. Teachers must have a solid foundation in both education and health sciences. Here are some key qualifications:
- Bachelor’s Degree: Typically in education, health education, or a related field.
- Teaching Certification: Valid teaching credentials specific to their state or country.
- Specialized Training: Courses or certifications in human sexuality, adolescent development, and psychology.
In addition to these qualifications, teachers should have strong interpersonal skills. They must be able to communicate complex topics in a simple, respectful manner. Experience with diverse student populations is also beneficial. Below is a table summarizing the essential qualifications:
| Qualification | Description |
|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree | In education, health education, or a related field |
| Teaching Certification | Valid credentials for the state or country |
| Specialized Training | Courses in human sexuality, adolescent development |
Ongoing Professional Development
Ongoing professional development is vital for sex education teachers. It helps them stay updated on the latest information and teaching methods. This continuous learning process involves several key areas:
- Workshops and Seminars: Regular attendance at workshops and seminars on sex education topics.
- Online Courses: Enrolling in online courses to learn new research findings and pedagogical strategies.
- Peer Collaboration: Engaging with fellow educators to share experiences and best practices.
Staying current with new information ensures that teachers provide the most accurate and relevant education. Professional development also helps teachers address emerging issues in sex education. For instance, topics such as consent, online safety, and LGBTQ+ inclusivity require continuous learning.
Below is a list of ongoing professional development activities:
- Attending annual sex education conferences
- Participating in peer review sessions
- Engaging in mentorship programs
These activities contribute to a teacher's ability to offer a well-rounded and up-to-date sex education curriculum. Investing in teacher training and development is essential for the ethical and effective delivery of sex education in schools.

Credit: aeon.co
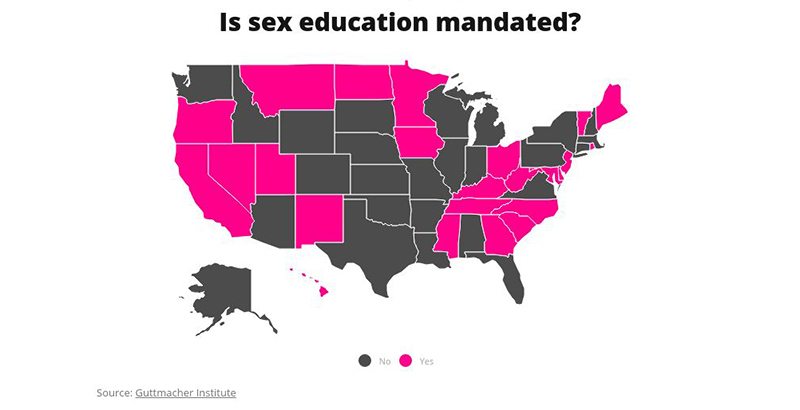
Legal Framework
Sex education in schools is a topic of much debate. The legal framework guiding this education plays a crucial role in what is taught. Different states have different laws and regulations. Understanding these can help parents, educators, and students know what to expect.
State Policies
Each state in the United States has its own policies for sex education. Some states mandate comprehensive sex education. Others leave it to local school districts.
In states with comprehensive sex education, students learn about:
- Human anatomy
- Reproductive health
- Sexual orientation
- Consent and healthy relationships
In contrast, some states focus on abstinence-only education. This means students are taught that abstaining from sex is the best choice. Topics like contraception and safe sex practices might be excluded.
Here is a brief comparison:
| Type of Education | Topics Covered |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive | Human anatomy, reproductive health, sexual orientation, consent, contraception |
| Abstinence-only | Abstinence as the best choice, often excludes contraception and sexual orientation |
State policies vary widely. Some states require parental consent for sex education. Others allow parents to opt their children out. Knowing your state's policies is important.
Rights Of Students
Students have rights when it comes to sex education. These rights ensure students receive accurate and age-appropriate information.
Some key rights include:
- The right to accurate information
- The right to privacy
- The right to ask questions
- The right to be free from discrimination
Accurate information is vital. Students need to know about their bodies, relationships, and health. This information helps them make informed choices.
Privacy is also important. Students should feel safe to ask questions without fear of judgment. Schools should create a safe environment for these discussions.
Discrimination in sex education can be harmful. All students should receive the same information, regardless of gender, sexual orientation, or background. Ensuring these rights can lead to better health and well-being for all students.
The legal framework around sex education is complex. Understanding state policies and students' rights can help navigate this important topic.
Ethical Dilemmas
Sex education in schools often stirs deep ethical debates. What should be taught? Who decides? These questions lead to ethical dilemmas. Schools need to balance moral values, cultural beliefs, and the well-being of students. This balance is not easy. Different communities have different views. Below, we dive into some of the key ethical dilemmas in sex education.
Consent Education
Teaching consent is vital. It helps students understand boundaries and respect. But how should schools approach this?
There are several key points to consider:
- Clarity: Consent must be clear and enthusiastic. It’s not just about saying "yes" or "no."
- Age Appropriateness: Materials should match the students' age. Younger students need simpler explanations.
- Role-Playing: Scenarios and role-playing can help. They teach students how to say "no" and how to respect a "no."
A table can help show the differences:
| Age Group | Consent Education Focus |
|---|---|
| Elementary | Personal space, saying "no" to unwanted touch |
| Middle School | Clear communication, understanding boundaries |
| High School | Sexual consent, respecting partners' decisions |
Teaching consent is not just about preventing abuse. It’s about fostering respect. It’s about building healthy relationships. This is an ethical responsibility.
Addressing Lgbtq+ Topics
Including LGBTQ+ topics in sex education is crucial. It ensures that all students feel seen and respected. But this inclusion comes with its own set of ethical challenges.
Here are some considerations:
- Inclusivity: All students should feel included. This means using language that respects everyone.
- Representation: Students should see their experiences reflected. This includes diverse relationships and identities.
- Support: Schools need to provide support. This includes counseling and safe spaces.
A table can help visualize the support needed:
| Area | Support Provided |
|---|---|
| Curriculum | Inclusive materials, diverse examples |
| Staff Training | Workshops, sensitivity training |
| Student Support | Counseling, peer support groups |
Addressing LGBTQ+ topics is more than just teaching facts. It’s about creating a safe environment. It’s about acceptance and understanding. This is an ethical necessity in modern education.
Future Trends
Sex education in schools is a subject of great importance. What should be taught in these classes often sparks debates. As society evolves, so do the trends in sex education. Future trends focus on being more inclusive and up-to-date. This ensures that all students receive accurate and helpful information.
Digital Resources
Digital resources are becoming essential in modern sex education. They provide students with interactive and engaging ways to learn. Here are some key points about digital resources:
- Accessibility: Digital platforms can be accessed anytime and anywhere, making learning more flexible.
- Interactive Content: Videos, quizzes, and games make learning more engaging. Students can interact with the content, which helps in better understanding.
- Up-to-date Information: Digital resources can be updated easily, ensuring that the information is current and accurate.
Several digital tools are making a significant impact:
| Tool | Feature |
|---|---|
| Apps | Provide information and quizzes on various topics |
| Websites | Offer detailed articles and videos for deeper understanding |
| Online Courses | Structured modules with assessments to track progress |
These tools help students learn at their own pace. They also ensure that the information is reliable and presented in a way that is easy to understand. Digital resources are shaping the future of sex education by making it more accessible and engaging.
Adapting To Social Changes
Adapting to social changes is crucial for effective sex education. Societal norms and values are constantly evolving. Sex education must reflect these changes to stay relevant. Here are some ways sex education can adapt to social changes:
- Inclusivity: Education should cover topics related to all genders and sexual orientations. This ensures that every student feels represented.
- Consent and Boundaries: Teaching about consent and personal boundaries is vital. It helps students understand the importance of mutual respect.
- Healthy Relationships: Focus on what makes relationships healthy. This includes communication, trust, and respect.
Social changes demand that sex education topics expand. Here are some examples:
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
| LGBTQ+ Issues | Understanding and respecting different sexual orientations and gender identities |
| Online Safety | Protecting oneself from online predators and understanding digital consent |
| Mental Health | Recognizing the connection between mental health and sexual well-being |
Adapting to these social changes ensures that sex education remains relevant and effective. It prepares students for the realities of today's world. By being inclusive and comprehensive, sex education can better support the diverse needs of students.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Sex Education?
Sex education teaches about human sexuality, including anatomy, reproduction, and sexual behavior. It aims to promote healthy and informed decisions.
Why Is Sex Education Important?
Sex education is vital for promoting safe practices, preventing STDs, and reducing unwanted pregnancies. It also encourages respectful relationships.
Who Decides Sex Education Curriculum?
Curriculum decisions are usually made by school boards, educators, and sometimes parents. State and national guidelines also influence the content.
Should Parents Be Involved In Sex Education?
Yes, parental involvement ensures that sex education aligns with family values. It fosters open communication between parents and children.
Conclusion
Sex education in schools remains a complex issue. Teaching it requires balance and sensitivity. Educators must consider cultural values and parental concerns. Comprehensive programs can promote healthy relationships and informed choices. Clear communication is essential. Schools play a critical role in this education.
Properly designed curriculums can benefit students greatly. They can reduce misinformation and promote safety. Collaboration between parents, teachers, and experts is key. Together, they can craft effective and ethical sex education.




0 Comments